-
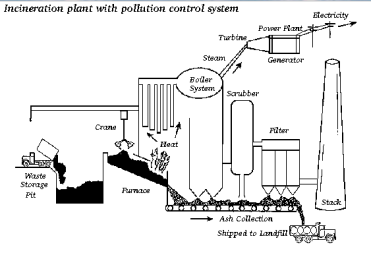
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials. Incineration and other high-temperature waste treatment systems are described as “thermal treatment”. Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas, and heat.
Incineration
A waste treatment technology, which includes the combustion of waste for recovering energy, is called as “incineration”. Incineration coupled with high temperature waste treatments are recognized as thermal treatments. During the process of incineration, the waste material that is treated is converted in to IBM, gases, particles and heat. These products are later used for generation of electricity. The gases, flue gases are first treated for eradication of pollutants before going in to atmosphere.
Among waste-to-energy technologies, incineration stands taller. Other technologies are gasification, PDG, anaerobic digestion and Pyrolysis. Some times Incineration is conducted with out the reason for recovering energy.
In past, incineration was conducted with out separating materials thus causing harm to environment. This un-separated waste was not free from bulky and recyclable materials, even. This resulted in risk for plant workers health and environment. Most of such plants and incinerations never generate electricity.
Incineration reduces the mass of the waste from 95 to 96 percent. This reduction depends upon the recovery degree and composition of materials. This means that incineration however, does not replace the need for landfilling but it reduced the amount to be thrown in it.
Incineration comes with a number of benefits in specific areas like medical wastes and other life risking waste. In this process, toxins are destroyed when waste is treated with high temperature.
Incineration or thermal treatment of waste is much popular in countries like Japan where there is scarcity of land. The energy generated by incineration is highly demanded in countries like Denmark and Sweden. In year, 2005 it was estimated that 4.8 percent of the electricity as is consumed by Danish nation was produced by incineration and the amount of heat was some 13.7 percent out of total. Other then Denmark and Sweden many European countries are recovering heat and electricity from waste.
[SOURCE:: http://www.wrfound.org.uk/articles/incineration.html]
IISC BANGALORE NPTEL INCINERATION NOTES:: lecture8MIT NOTES ON INCINERATION:::BOOKS LINKS RELATED INCINERATION::RULES AND REGULATION FOR SOLID WASTE INCINERATION BY EPA::::
- Comment
- Reblog
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.